Zepbound Weight Loss: Obesity is a global problem; all over the world, it impacts millions of adults every day, and certain shirk risk factors include heart attack, diabetes, and specific cancers.
In response to this epidemic, pharmaceutical companies are constantly developing new treatments for weight management. Zepbound is one such breakthrough weight loss drug recently approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
This article offers an in-depth look at Zepbound, including its active ingredient, effectiveness, side effects, and comparisons to other weight loss drugs like Mounjaro, Ozempic, and Wegovy.
What is Zepbound Weight Loss?
Zepbound, a weight loss medication marketed under the brand name tripeptide, was developed by Eli Lilly and is mainly used for moderate to long-term weight control in overweight or obese adults.
Zepbound offers a different perspective on weight loss for those with ethnicity issues for those with ethnicity issues: using specific metabolic pathways to achieve better results than any previous weight-loss method.
Zepbound’s active ingredient, tripeptide, is a dual glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist.
In other words, it mimics the action of some hormones that regulate appetite or sugar levels in the blood. This dual character accounts for Zepbound ‘s effectiveness on adults who need to lose weight.
How Does Zepbound Work?
By mimicking the hormones in the brain that control hunger and food intake, Zepbound helps people eat less. The drug is given once a week and works on GIP and GLP-1 receptors in the brain. These receptors sense fullness and are within our bodies ‘natural satiety system.
By stimulating them, Zepbound doesn’t eradicate food cravings where they occur but decreases them somewhat while helping to make us feel that we have had enough food to eat after a meal.
Clinical trials have demonstrated that people who use Zepbound can achieve significant weight loss. For instance, Zepi mou Mile Zib is reported to be far more appealing than Adiphene and Oramo.
In these studies, participants who took Zepbound lost an average of 22.5% of their body weight over 72 weeks, which is a significant reduction when compared to those who did not receive the drug. What’s particularly striking about this is other drugs like Ozempic and Wegovy typically have an average weight loss of just 15-17%.
Who Can Use Zepbound?
Zepbound is intended for overweight adults (defined as individuals with a body mass index (BMI) of 30 kg/m2 or more) or those with a BMI between 27 kg/m2 and 30 kg/m2 and at least one weight-related condition, such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and hypercholesterolemia.
The medication is part of a comprehensive weight management program that includes better diets, more significant exercise, and behavioral modifications.
However, not every person can use Zepbound. It is contraindicated for those with personal or family histories of certain types of thyroid tumors, particularly medullary thyroid carcinoma.
It should not be given twice daily to patients having experienced an allergic reaction to tripeptide in the past. Women who are pregnant, as well as those hoping to become pregnant, should avoid using Zepbound because the implications for an unborn baby are still not fully understood.
How to Use Zepbound
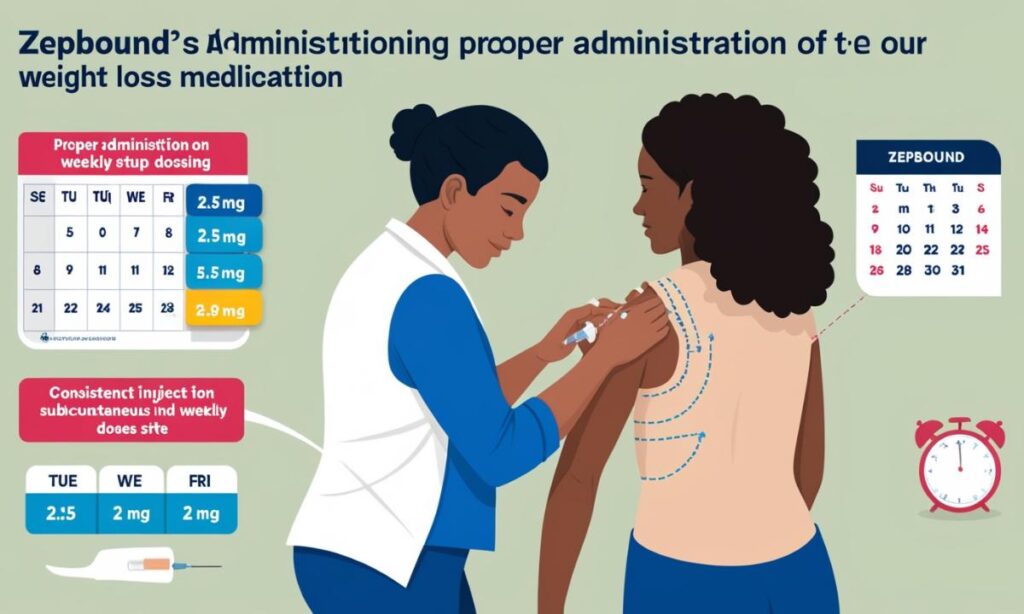
It is administered subcutaneously, which means it is given under the skin. An injection is usually given into the abdomen, thigh, or other suitable site. The starting dose is 2.5 mg once a week. The dose can gradually increase based on the patient’s response and tolerance. Patients must follow the healthcare provider’s instructions carefully and not exceed the recommended dosage.
Patients should give Zepbound on the same day each week so that drug levels in their bloodstream remain constant.
If a dose is missed, take it as soon as possible, within four days of the missed dose. If more than four days have passed, the patient should skip the missed dose and resume their regular dosing schedule.
Potential Side Effects of Zepbound
- Nausea is the most frequently reported side effect and usually occurs during the initial weeks of treatment.
- Diarrhea: Some patients may experience gastrointestinal issues, particularly in the early stages of taking Zepbound.
- Vomiting: This side effect tends to be mild and temporary but can be bothersome for some individuals.
- Constipation: A common side effect that can usually be managed with dietary changes and hydration.
- Injection site reactions can include redness, swelling, or itching at the injection site.
There are also severe potential side effects, including:
- Pancreatitis: Inflammation of the pancreas can occur and may present as severe abdominal pain.
- Hypoglycemia: Especially in patients with type 2 diabetes who are also taking other glucose-lowering medications.
- Kidney problems: Changes in kidney function have been observed, particularly in patients with existing kidney issues.
- Allergic reactions: Severe allergic reactions are rare but can occur, requiring immediate medical attention.
Effectiveness of Zepbound for Weight Loss
Refined clinical trial data show that Zepbound is effective in helping consumers achieve dramatic weight reductions in their fat reserves.
It has been shown “to help people lose on average 22.5% of their body weight,” making Zepbound one of the most effective drugs available for weight control today.
This weight loss comes from a reduced appetite and feeling that one has eaten enough, combined with better functioning of the body’s metabolism.
Zepbound ‘s effectiveness has been compared with weight-loss medications such as Mounjaro, Ozempic, and Wegovy.
All of these drugs are successful in perking up fat burning. However, bringing more into reality the results one wants to achieve, Zepbound has been found to give better results on the average amount lost by people than any other medication. Moreover, Zepbound’s unique mode of action on GIP and GLP-1 receptors may increase their chances in patients unsuitable for different therapies.
Zepbound vs. Mounjaro: Understanding the Differences
Zepbound and Mounjaro are used for weight control, but the medicines also differ. Mounjaro, better known by its generic name tripeptide, is designed to treat type 2 diabetes. It is also being tried out on overweight people as an off-label use.
The only difference lies in their regulatory approvals and how they are sold. Both drugs use the same active ingredient but differ in branding and marketing.
The differentiation lies in their approvals and marketing. Zepbound is marketed mainly for weight loss, while Mounjaro targets diabetes patients’ glycemic control.
Nevertheless, both medications have shown promising results in reducing body weight with a similar side-effect profile.
Cost and Accessibility of Zepbound
Patients might hesitate because the cost of Zepbound could be unaffordable. This price won’t come cheap. Its coverage depends on the insurance plans its users attach to.
Some insurance plans do not cover Zepbound, a weight loss medication. This isn’t the case for other plans with the results, as we seem to be cashed out daily.
Eli Lilly, the maker of Zepbound, offers patient assistance programs and discounts to make the medication more affordable. Patients are advised to inquire about specific coverage options from their healthcare providers.
Who Should Avoid Zepbound?
While Zepbound is generally safe for most adults with obesity, specific individuals should avoid using this medication:
- Pregnant or planning to become pregnant: It is not known if Zepbound passes into breast milk or how it might affect a baby while using Zepbound.
- Individuals with a history of thyroid cancer: Zepbound may increase the risk of thyroid tumors in these patients.
- Those with a history of pancreatitis: Since the medication can increase the risk of pancreatitis, it is not recommended for individuals with a history of this condition.
Patients should discuss their medical history with their healthcare provider to determine whether Zepbound is the right option.
Can Zepbound Cause Hair Loss?
The potential side effects of weight-loss drugs—such as shedding one’s mane—are always an all-too-obvious concern for the consumers.
However, there is no substantial evidence linking hair loss with Zepbound, although occasionally, people who follow this kind of diet experience changes in body shape. The quality of one’s hair is just another matter.
A man taking Zepbound may become thinner, but conversely, no direct cause-and-effect relationship exists between it and hair loss. Patients who have lost hair should consult with a doctor to eliminate the possible causes of new options for weight reduction in adult populations struggling to lose weight. Zepbound’s two-action mechanism on the GIP and GLP-1 receptors brings unique benefits, significantly reducing body weight and improving metabolic health.
What’s more, Zepbound is no exception in this regard. Just as every other medication has risks and side effects of its own – some potentially severe indeed – anybody considering whether it would be wise for them to take this drug should consult their doctor first.
My Opinion
Whether you are taking medication or not, zepbound brings to people who never thought that they could have a chance at weight loss another way out. Zepbound is an essential part of any comprehensive weight management program for people with obesity problems.
Through appropriate medication use, recommended dietary programs, and regular physical exercise, it is possible for individuals to gradually lose the extra pounds in a safe and effective manner while extending their lives overall.



















Leave a Reply
View Comments